+917906530711

This is your website preview.
Currently it only shows your basic business info. Start adding relevant business details such as description, images and products or services to gain your customers attention by using Boost 360 android app / iOS App / web portal.
Introduction: Dental caries, commonly known a...
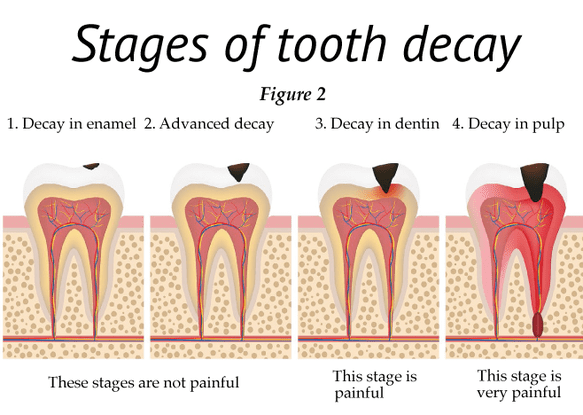
Introduction: Dental caries, commonly known as tooth decay or cavities, is a prevalent oral health issue that affects people of all ages. Dr. Navratna Singh is here to provide you with essential information about dental caries, its progression, potential consequences, and how to prevent and treat it effectively. Dental Caries Progression: Dental caries is a dynamic process that occurs in stages: Demineralization: It starts with the accumulation of plaque and bacteria on the tooth's surface. The bacteria produce acid when exposed to sugars and carbohydrates in your diet. This acid gradually erodes the enamel, leading to demineralization. Cavitation: As the enamel breaks down, a cavity or hole begins to form in the tooth. This is the stage where most people start experiencing pain or sensitivity. Invasion of Dentin: If left untreated, the decay can progress to the dentin, the layer beneath the enamel. Dentin is less resistant to acid, causing the cavity to expand more rapidly. Pulp Involvement: In severe cases, the decay can reach the dental pulp, where the nerves and blood vessels reside. This stage is often associated with intense pain and the potential for infection. Sequelae of Dental Caries: Dental caries can lead to several sequelae, including: Toothache: Pain is a common consequence of untreated dental caries, and it can become excruciating when the decay reaches the pulp. Infections and Abscesses: Bacterial invasion of the dental pulp can lead to abscess formation, which may require more extensive dental treatment. Tooth Loss: Severe decay can result in the loss of the affected tooth, impacting your ability to chew and speak. Systemic Health Issues: Dental caries can have implications for your overall health, as oral infections can spread to other parts of the body. Prevention and Treatment: Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque and prevent the buildup of harmful bacteria. Dietary Choices: Reduce the consumption of sugary and acidic foods and drinks, as they contribute to the formation of cavities. Regular Dental Check-ups: Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups. Early detection of caries can prevent them from progressing. Fluoride: Fluoride strengthens enamel and can be applied topically or ingested through fluoridated water and toothpaste. Sealants: Dental sealants can be applied to the chewing surfaces of molars to prevent decay. Restorative Dentistry: If caries are detected, various treatments like fillings, root canals, and crowns can restore your tooth's health and function. Good Oral Habits: Encourage children to establish good oral hygiene habits from a young age to prevent caries. Conclusion: Understanding the progression, consequences, and preventive measures for dental caries is essential for maintaining good oral health. Dr. Navratna Singh recommends practicing good oral hygiene, making wise dietary choices, and seeking professional dental care to keep your smile healthy and beautiful. Remember, early prevention and treatment are key to avoiding the sequelae of dental caries and ensuring a lifetime of healthy teeth

